New Applications for Your Mobile Device for Pediatric Anesthesia: The Pedi Crisis App
By Anna Clebone, MD
Rainbow Babies and Children’s Hospital
Cleveland, OH
I’d like to introduce a technology column for this newsletter: “New Applications for Your Mobile Device for Pediatric Anesthesia”. Each quarter, I’ll review another application that can be downloaded to your iPhone or Android device that could be useful to the pediatric anesthesiologist in the operating room. This spring, I’ll review the ‘Pedi Crisis App’, which was created at the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, based on the Pediatric Critical Events Checklists from the Society for Pediatric Anesthesia. The ‘Pedi Crisis App’ can be downloaded for free from the App Store on the iPhone or Android.
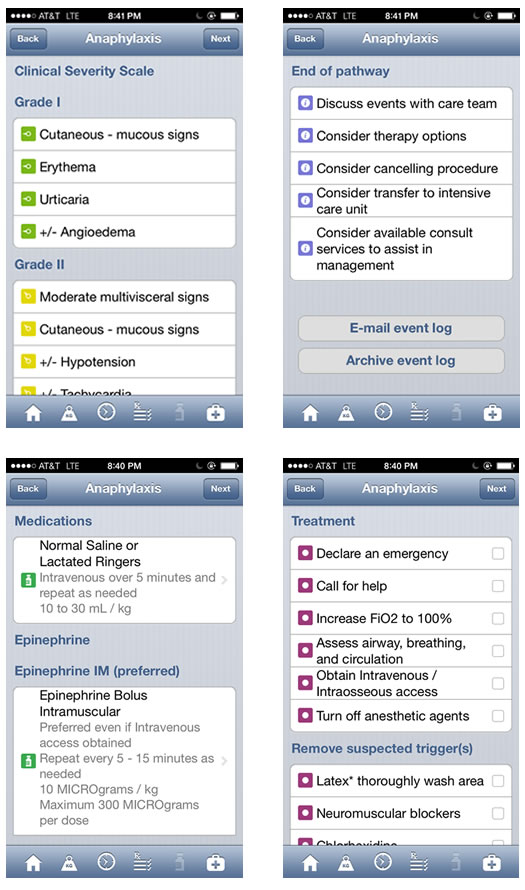
The Pedi Crisis App contains algorithms for individual types of emergencies, and can also be used for teaching medical students and residents how to handle crisis situations. Peer-reviewed algorithms for treating 18 different pediatric crisis situations are just a ‘click’ away on your pocket device. The mobile app has an advantage over the paper algorithm in that users are led through the algorithm in an interactive format, for example, the ‘hypotension’ algorithm has options for ‘decreased preload’, ‘decreased contractility’, and ‘decreased afterload’, and the user is directed to the correct treatment for each.
The patient’s weight and age are also entered, so that dosing and expected vital signs values can be automatically calculated. Specific, pertinent, potentially life saving details are given for the treatment selected, such as ‘avoid calcium channel blockers’ when administering dantrolene in the MH algorithm. Debriefing, a crucial step after any critical event, is made easy by the fact that a tally is made of the meds administered and options selected, which can be e-mailed automatically to the user. The 18 different crises algorithms contained in the app are:
- air embolism
- anaphylaxis
- bradycardia
- cardiac arrest
- difficult airway
- fire (airway and OR)
- hyperkalemia
- hypertension
- hypotension
- hypoxia
- local anesthetic toxicity
- loss of evoked potentials
- malignant hyperthermia
- myocardial ischemia
- tachycardia
- transfusion and reactions
- trauma


